PACKAGES
Search inspection programs

Ankle-Brachial Index (ABI) Examination
Ankle-Brachial Index (ABI) Examination
ค่าตรวจ 200 บาท (จากปกติ 1,200 บาท) ตั้งแต่ 1 ม.ค. – 31 ธ.ค. 2568
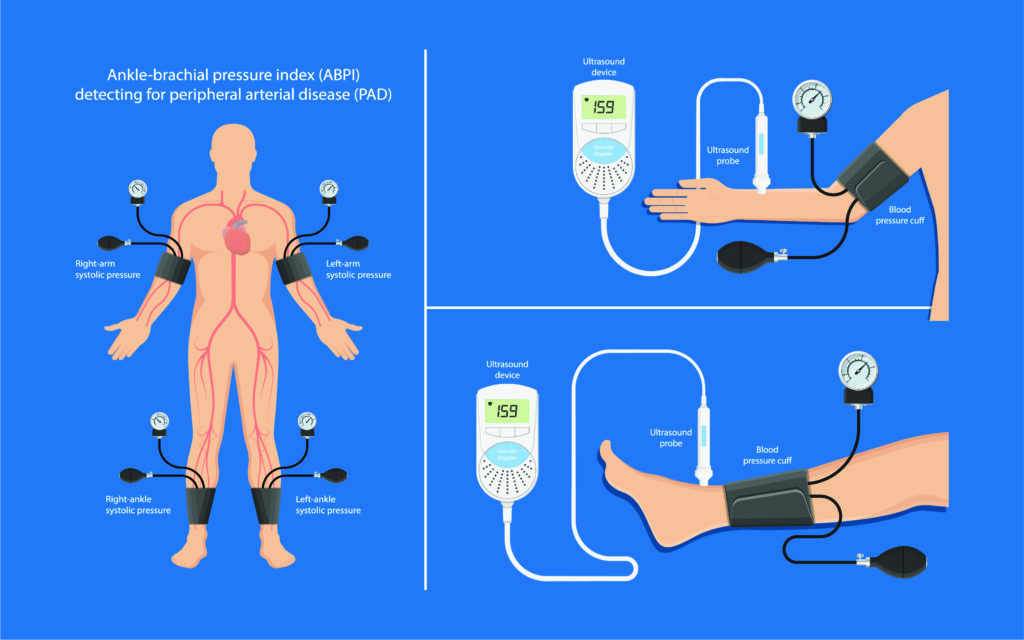
ABI examination is similar to measuring blood pressure. It is easy, convenient, and quick, providing high accuracy without any discomfort or pain during the examination. It compares the blood pressure between the arteries in the arms and the arteries in the ankles.
Benefits
- Assess blockages in the arteries and flexibility of blood vessels.
- Aid in the diagnosis and early detection of peripheral arterial disease, which often occurs along with blockages in the arteries supplying the heart and brain (especially in individuals with diabetes, smoking history, or leg pain). It can also help identify other significant diseases such as coronary artery disease or carotid artery disease, which can lead to stroke and death.
- Predict the risk of developing cardiovascular diseases in the future. Studies have shown that individuals with an abnormal ABI at an average age of 66 have a significantly higher risk of cardiovascular diseases and four times higher risk of death from heart disease compared to those with a normal ABI.
- Assess the severity of arterial stiffness.
- Evaluate treatment outcomes.
Individuals who should undergo ABI examination:
- Patients with peripheral artery disease and coronary artery disease.
- Patients with diabetes, high blood pressure, high cholesterol, or obesity (BMI greater than or equal to 25).
- Patients who are unable to walk and bedridden.
- Patients with elevated levels of certain substances in the blood, such as homocysteine and lipoprotein.
- Smokers or individuals who have smoked for more than 10 years (including second-hand smokers).
- Older adults or individuals over 60 years old (those under 60 years old have a less than 3% chance of developing peripheral arterial disease, but individuals over 70 years old have a more than 20% chance, regardless of gender).
- Individuals with a family history of coronary artery disease and stroke before the appropriate age.

